
Introduction to Alginate-Based Food Encapsulation
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR BLOG
Promotions, new products, and recipes.
Above: Brown seaweed, the source of alginate, a versatile material revolutionizing food encapsulation.
In today's era, where food preservation and innovation are paramount, the concept of food encapsulation has emerged as a transformative technique within the modern food industry. As consumer preferences evolve to demand extended shelf life, controlled flavor release, and enhanced nutrient delivery, the art of encapsulation takes center stage. At the heart of this revolution lies alginate, a versatile substance sourced from brown seaweeds, offering a range of advantages that directly address the challenges of preserving and delivering food.
Key Takeaways
- In this comprehensive exploration, we'll embark on an illuminating journey into the realm of alginate-based food encapsulation.
- We'll uncover its origins, delve into its properties, uncover the intricacies of the encapsulation process,
- We will explore its applications and benefits, address the associated challenges, and glimpse into the promising trends that lie ahead. Here's an overview of the enlightening voyage that awaits:
Explore Alginate's World:
Understanding the natural origins and gelling properties of alginate is crucial. Derived from brown seaweed, alginate's exceptional ability to form gels finds use in creating stable matrices that extend shelf life and regulate controlled release. This segment unveils the science behind this phenomenon, showcasing how alginate transforms bioactive compounds into protective capsules that redefine modern food experiences.
Applications Unveiled:
The spectrum of applications for alginate encapsulation is as diverse as it is promising. It stands as a sentinel against oxidation, moisture loss, and degradation processes, significantly prolonging the shelf life of perishable foods. Moreover, it reimagines flavor delivery, ensuring the orchestrated release of flavors in products ranging from beverages to confectionery and snacks.
Alginate's versatility extends to the realm of functional foods, offering a solution to the challenge of preserving sensitive nutrients in fortified products. The concept of targeted release emerges as a new paradigm, wherein encapsulated compounds are released strategically during digestion or absorption, maximizing their efficacy.
Future and Impact:
Envisioning the future of alginate encapsulation is a fascinating endeavor. As the integration of nanotechnology promises heightened precision and efficiency in encapsulation techniques, the potential for creating more targeted delivery systems becomes evident.
Sustainable sourcing practices align with the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions, ensuring a continuous supply of seaweed for alginate extraction. The prospect of personalized nutrition is another horizon that beckons, where alginate encapsulation tailors dietary experiences to individual needs. As we navigate the path ahead, we recognize that alginate encapsulation holds the promise of reshaping food preservation, delivery, and personalized nutrition. It is a journey that considers challenges, embraces sustainability, and ushers in a new era of culinary innovation.
Unveiling Alginate's Nature:
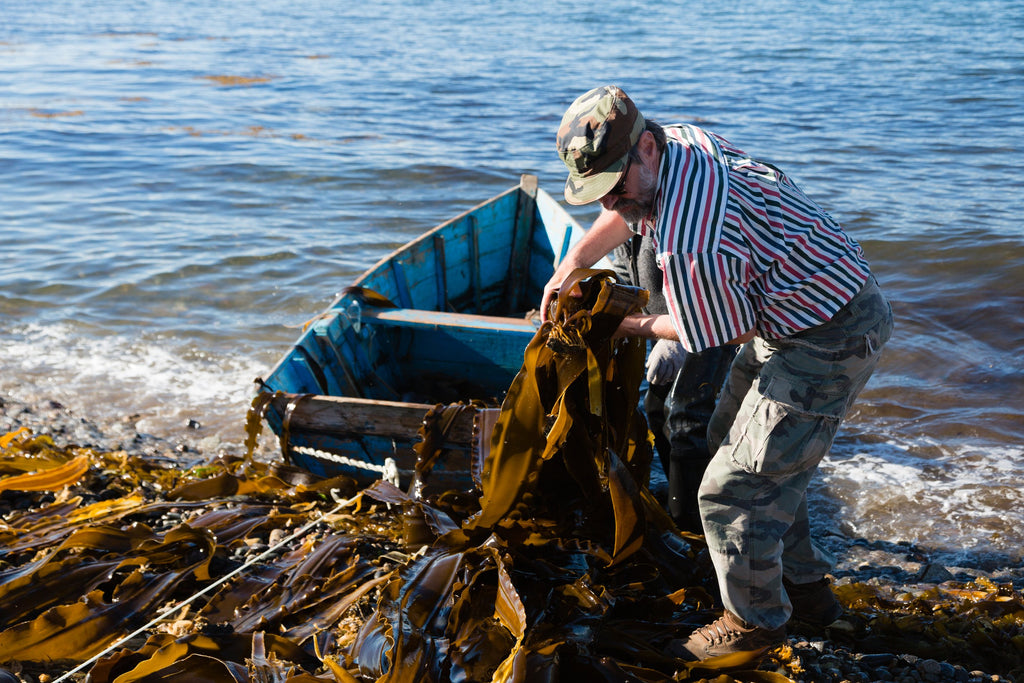 Unloading giant kelp, the raw material from which alginate is refined.
Unloading giant kelp, the raw material from which alginate is refined.
Alginate, a natural polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed, possesses a remarkable gelling ability that positions it as an ideal candidate for encapsulation. This gelling process is a result of its interaction with divalent cations, particularly calcium, leading to the formation of a gel network that encapsulates and protects active compounds.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has affirmed the safety of alginate consumption, designating it as a generally recognized safe (GRAS) ingredient. Furthermore, the diverse types of alginates available, each with distinct properties, highlight the material's versatility. From high-G to low-G alginates, the customization potential is evident, offering a tailored approach to food innovation.
The Art of Alginate-Based Food Encapsulation:
The encapsulation process involves combining bioactive compounds with alginate, forming droplets, and crosslinking with calcium ions to create stable matrices.
The encapsulation process is an intricate ballet that involves entrapping bioactive compounds within alginate matrices, safeguarding them against external factors. This choreography commences with the mixing of desired bioactive components and alginate, forming droplets that are then crosslinked using calcium ions. The core material's nature holds the key, be it flavors, nutrients, or enzymes, to determining the purpose of the encapsulation.
This process, while complex, results in encapsulated products that offer enhanced stability, controlled release, and protection of valuable components. Alginate's role as a guardian ensures that the encapsulated ingredients retain their integrity until the desired moment of consumption.
Diverse Applications of Alginate Encapsulation:
Alginate is a cell wall component of marine brown algae
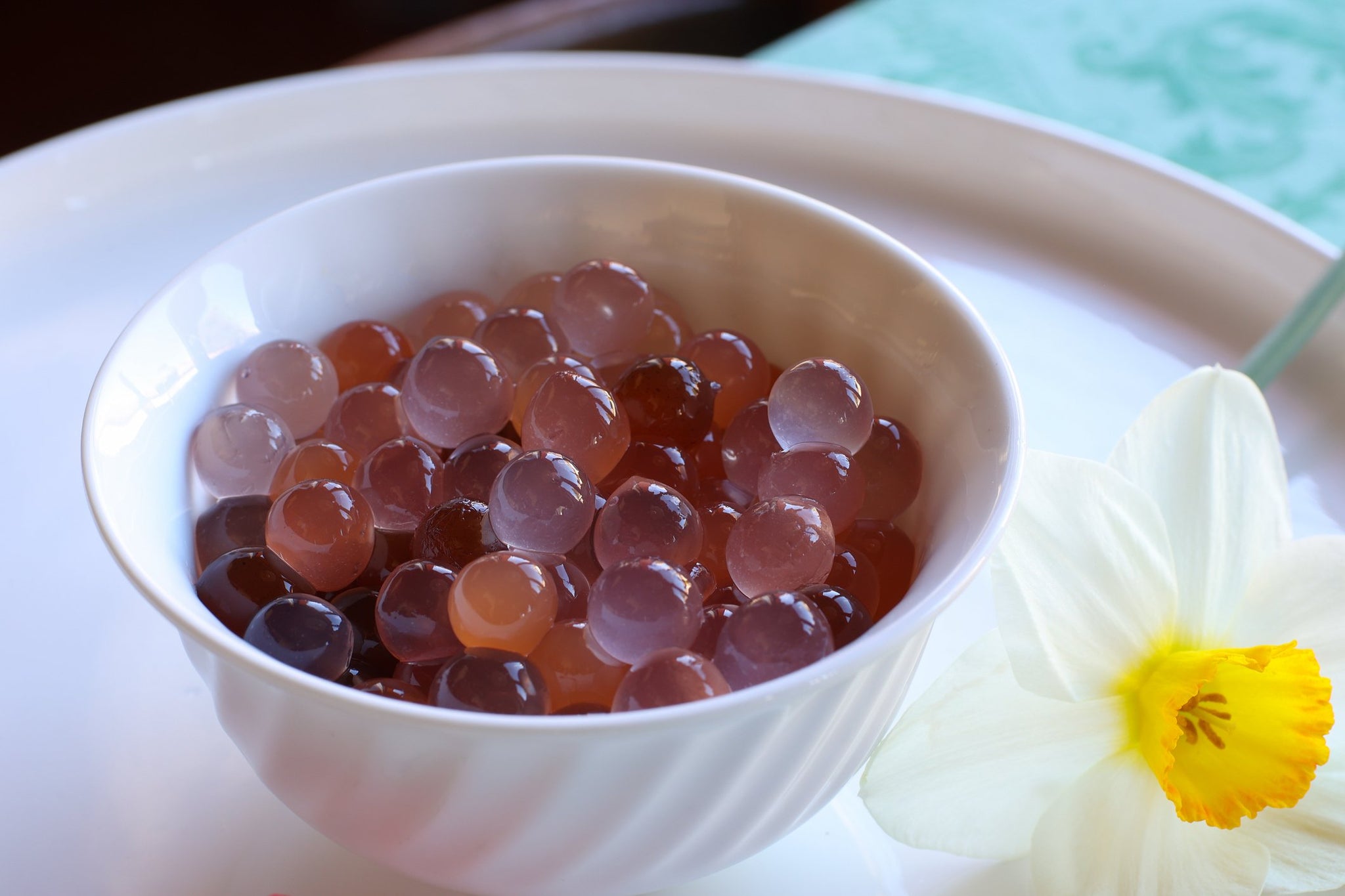

A group of sodium alginate encapsulated spheres obtained by inverse spherification.
The capabilities of alginate encapsulation are as diverse as the culinary landscape itself. By preventing oxidation, moisture loss, and other detrimental processes, it bestows the gift of extended shelf life upon perishable foods. This attribute has transformative implications for food industries, reducing waste and enabling the provision of high-quality products to consumers.
The realm of flavor delivery also undergoes a revolution through alginate encapsulation. Products like beverages, confectionery, and snacks benefit from controlled release, ensuring that the flavor experience is both intense and predictable. Alginate, as an artful conductor, orchestrates taste sensations like never before.
Benefits and Advantages:
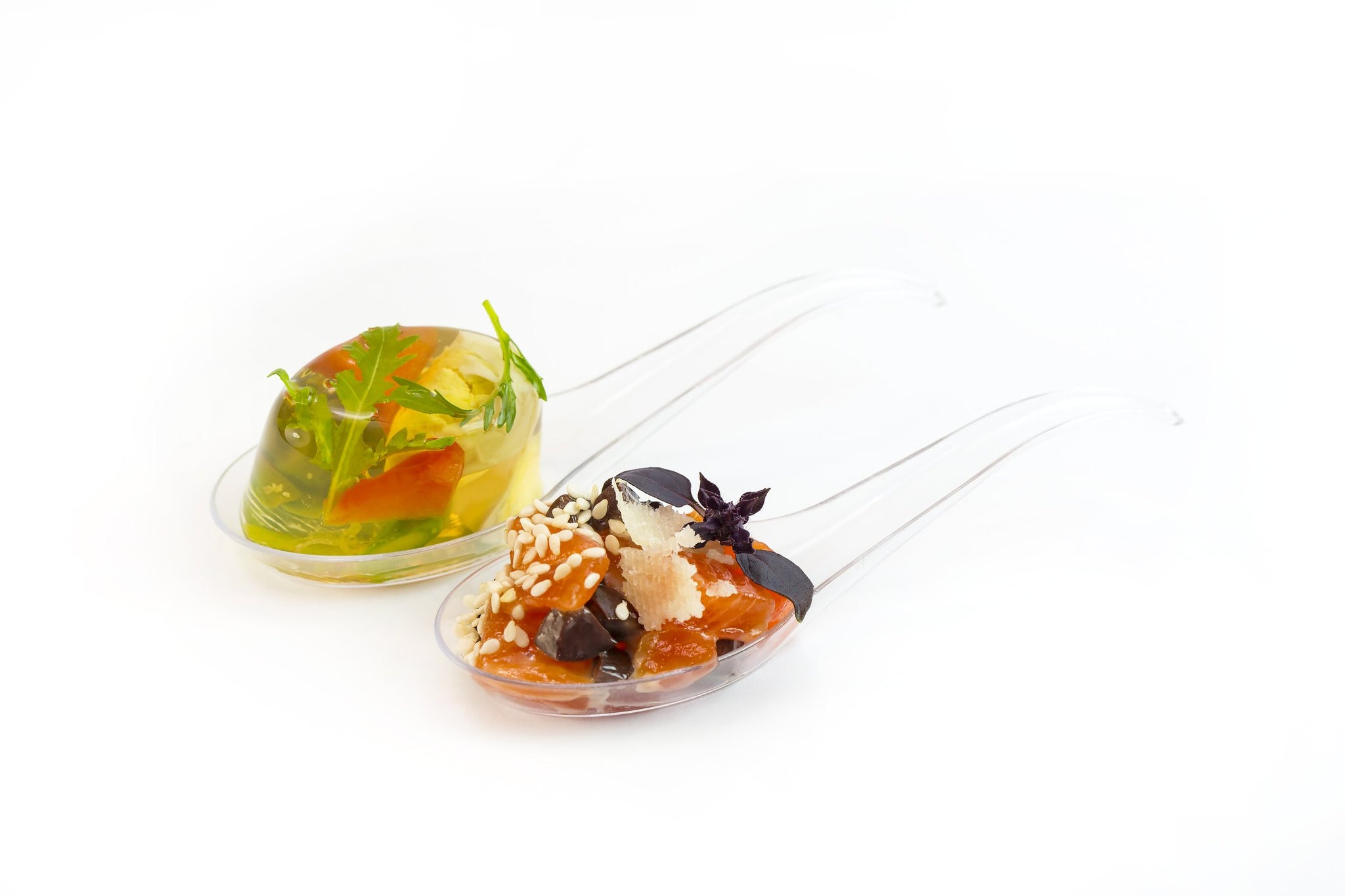

Alginate encapsulation preserves sensitive nutrients in fortified foods, ensuring their bioavailability upon consumption.
Alginate-based encapsulation offers a myriad of benefits that span from improved bioavailability to an elevated sensory experience. Poorly water-soluble compounds, often challenging to absorb, find an ally in encapsulation. It enhances their bioavailability, facilitating their absorption within the body and unlocking their full potential.
The controlled release facilitated by alginate encapsulation enhances the sensory journey for consumers. Flavors are released in a synchronized manner, enriching taste experiences and elevating the overall enjoyment of food products. Moreover, the prevention of unwanted interactions among ingredients safeguards the quality and integrity of the final product.
Challenges and Considerations:
Even as alginate encapsulation presents a world of possibilities, challenges weave through its tapestry. The quest to maintain structural stability across varying pH and temperature conditions is ongoing. This challenge is particularly relevant as encapsulated products navigate the dynamic environment of the digestive system.
Scalability and consistent production pose additional considerations. Transitioning from laboratory-scale to large-scale production requires meticulous planning to ensure uniformity across batches.
Consumer perception forms an integral part of the puzzle. While encapsulation enhances products, consumer understanding and acceptance need to be nurtured. Transparent communication about the encapsulation process bridges the gap between innovation and consumer trust.
Future Trends and Innovations:
The horizon of alginate encapsulation's future is adorned with innovative possibilities. The integration of nanotechnology into encapsulation techniques promises to enhance precision and efficiency. This fusion could lead to encapsulation systems that navigate with unparalleled accuracy through the intricate landscapes of the human body.
Sustainable practices, including responsible sourcing of seaweed for alginate extraction, pave the path for a more ecologically conscious future. This aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly solutions that resonate with modern consumers.
The concept of personalized nutrition takes center stage as well. Alginate encapsulation opens doors to crafting dietary experiences that are tailored to individual needs, thereby revolutionizing the landscape of nutritional consumption.
Conclusion:
As we reflect on this captivating voyage into the realm of alginate-based food encapsulation, a resounding truth emerges – the potential of this technique is nothing short of transformative. Its ability to redefine shelf life, amplify flavor delivery, and safeguard essential nutrients stands as a testament to human ingenuity.
Alginate encapsulation is poised to drive a paradigm shift in the culinary domain. It empowers us to envision a future where food preservation and delivery are elevated to an art form. The trajectory is clear – the boundaries of innovation will continue to expand, powered by the versatile capabilities of alginate.
As we bid farewell to this exploration, we stand at the crossroads of evolution and promise. Alginate encapsulation holds the key to a future where food science meets artistry, redefining how we experience and savor our meals.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What is the essence of food encapsulation, and why does it hold significance in the food industry?
A1: Food encapsulation revolves around the encapsulation of bioactive elements within protective matrices. This technique addresses contemporary consumer demands for prolonged shelf life, precise flavor release, and advanced nutrient preservation in food products.
Q2: How does alginate contribute to the realm of food encapsulation?
A2: Alginate, sourced from brown seaweed, boasts distinctive gelling properties upon interaction with calcium. This unique characteristic enables alginate to create protective barriers around active compounds, effectively addressing challenges in food preservation and delivery.
Q3: What are the primary challenges associated with alginate-based encapsulation?
A3: Challenges encompass maintaining the structural stability of encapsulated compounds under varying conditions, ensuring smooth and consistent large-scale production, and managing potential shifts in consumer perception due to the use of encapsulated ingredients.
Q4: What is the vision for alginate encapsulation's future impact?
A4: Alginate encapsulation's future is vibrant with innovation. The integration of nanotechnology promises heightened efficiency, while sustainable sourcing practices ensure the availability of seaweed for alginate extraction. Additionally, the concept of personalized nutrition holds the potential to transform dietary habits through tailored encapsulated compounds.
As we conclude this voyage through the world of alginate-based food encapsulation, we unveil its intrinsic nature, explore its applications, and recognize the challenges it surmounts. The horizon is promising, as innovation propels the boundaries of encapsulation techniques. As we step forward, we stand at the threshold of a future where alginate encapsulation heralds transformative change, reshaping the very core of how we encounter and relish our food.


|
About the Author Ed is the founder of Cape Crystal Brands, editor of the Beginner’s Guide to Hydrocolloids, and a passionate advocate for making food science accessible to all. Discover premium ingredients, expert resources, and free formulation tools at capecrystalbrands.com/tools. — Ed |
Enjoyed this post? Subscribe to The Crystal Scoop
Food-science tips, ingredient know-how, and recipes. No spam—unsubscribe anytime.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.



